This article explains how to use the HSB (Hue, Saturation, Brightness) Color Atlas to select, identify, and reproduce colors accurately for digital design and printing applications. The HSB Color Atlas provides a systematic way to explore and reference colors based on intuitive, human-perceived parameters. Download the color atlas here.
How to Use the HSB Color Atlas
Step 1: Open or Print the Atlas
The HSB Color Atlas can be used digitally (e.g., in Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, or PDF viewer) or as a printed reference.
If printing, ensure the printer is calibrated and a color profile (such as AdobeRGB or sRGB) is properly assigned to maintain accuracy.
Step 2: Understand the Layout
The atlas is typically divided by Hue pages, each representing a range of color hues (e.g., Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Cyan, Blue, Magenta).
Within each page:
Horizontal axis: Represents changes in Saturation (from low to high).
Vertical axis: Represents changes in Brightness (from high to low).
This layout allows you to quickly find variations of a specific hue with different intensities and brightness levels.
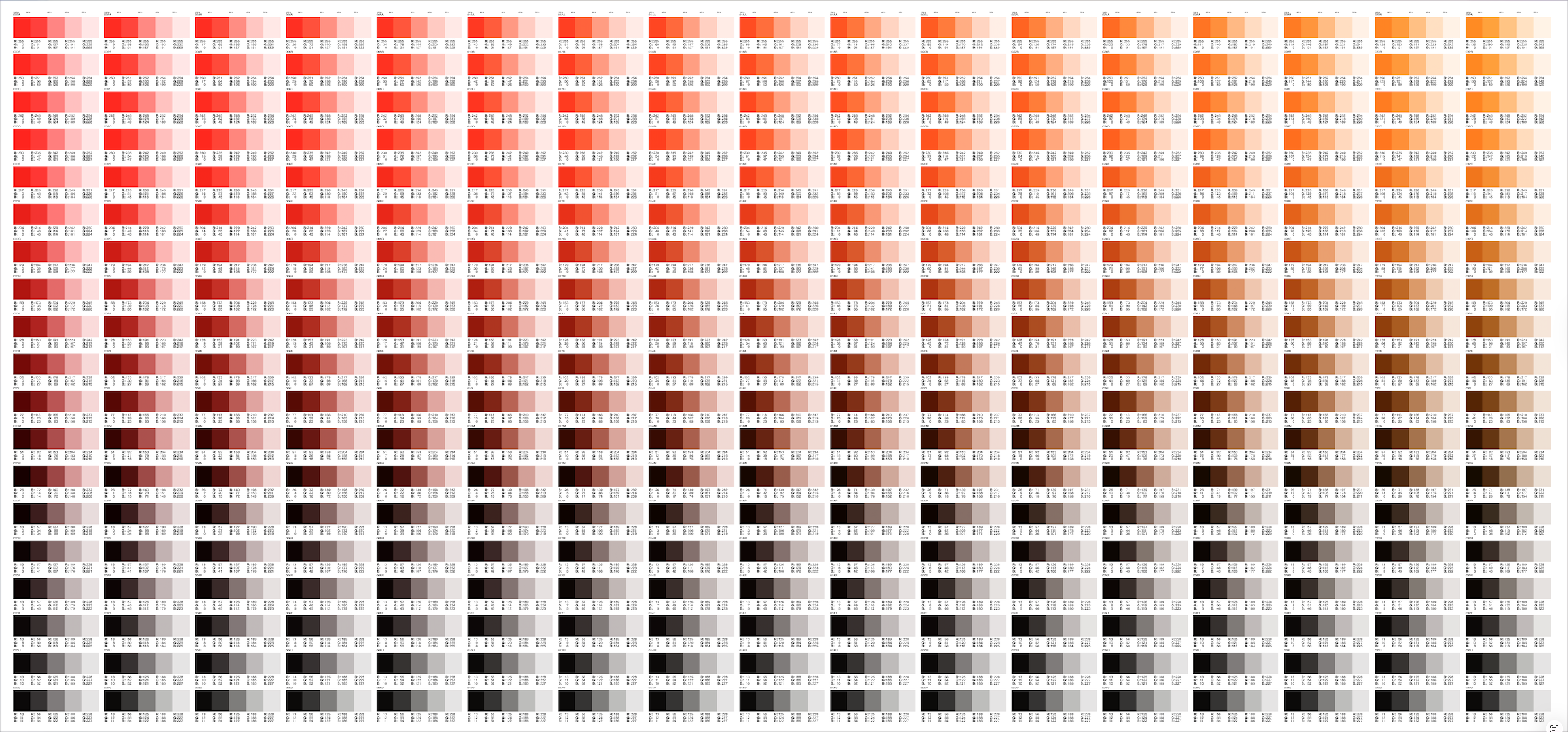
Step 3: Select a Color
Identify the Hue page closest to your desired color family (for example, H=200° for sky blue).
Move horizontally to adjust Saturation until the color looks as vivid or muted as needed.
Move vertically to adjust Brightness for lighter or darker shades.
Each color swatch includes HSB values (and often RGB or CMYK equivalents) for easy reference and digital reproduction.
Step 4: Record or Apply the Color
Once you’ve identified the desired swatch:
Note the HSB values or the color code provided.
In design software (e.g., Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign), open the Color Picker and enter the Hue, Saturation, and Brightness values directly.
Alternatively, use the RGB or CMYK equivalents if required for specific workflows.
Step 5: Assign or Convert Profiles (Optional)
When using the color atlas for printing, always ensure the correct ICC color profile is applied (e.g., AdobeRGB, sRGB, or a custom printer profile).
To match print and screen colors, convert or soft-proof the document using the same color space as your output device.
